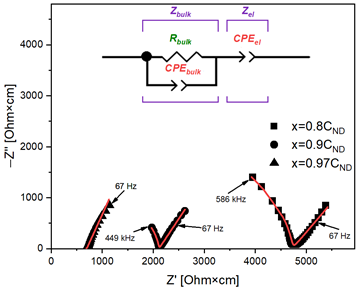
Transport and structural properties of (CH3)4NBF4 with nanodiamonds filler
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Zhang Z, Wang X, Li X, Zhao J, Liu G, Yu W, Dong X, Wang J. Review on Composite Solid Electrolytes for Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Mater Today Sustain. 2023;21:100316. doi:10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100316
Dirican M, Yan C, Zhu P, Zhang X. Composite Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2019;136:27–46. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2018.10.004
Liu Q, Jiang L, Zheng P, Sun J, Liu C, Chai J, Li X, Zheng Y, Liu Z. Recent Advances in Stability Issues of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes and Composite Solid Electrolytes for All‐Solid‐State Batteries. Chem Rec. 2022;22(10):e202200116. doi:10.1002/tcr.202200116
Voropaeva DYu, Stenina IA, Yaroslavtsev AB. Solid-State Electrolytes: A Way to Increase the Power of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Russ Chem Rev. 2024;93(6):RCR5126. doi:10.59761/RCR5126
Xue S, Chen S, Fu Y, Zhu H, Ji Y, Song Y, Pan F, Yang L. Revealing the Role of Active Fillers in Li‐ion Conduction of Composite Solid Electrolytes. Small. 2023;19(46):2305326.
Kumaravel V, Bartlett J, Pillai SC. Solid Electrolytes for High-Temperature Stable Batteries and Supercapacitors. Adv Energy Mater. 2021;11(3):2002869. doi:10.1002/aenm.202002869
Uvarov NF. Composite Solid Electrolytes: Recent Advances and Design Strategies. J Solid State Electrochem. 2011;15(2):367–389. doi:10.1007/s10008-008-0739-4
Liu S, Liu W, Ba D, Zhao Y, Ye Y, Li Y, Liu J. Filler‐integrated Composite Polymer Electrolyte for Solid‐state Lithium Batteries. Adv Mater. 2023;35(2):2110423.
Zheng F, Li C, Li Z, Cao X, Luo H, Liang J, Zhao X, Kong J. Advanced Composite Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries: Filler Dimensional Design and Ion Path Optimization. Small. 2023;19(21):2206355. doi:10.1002/smll.202206355
Ponomareva VG, Bagryantseva IN, Shutova ES. Hybrid Systems Based on Nanodiamond and Cesium Dihydrogen Phosphate. Mater Today Proc. 2020;25:521–524. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.304
Kubataev ZYu, Gafurov MM, Rabadanov KSh, Amirov AM, Akhmedov MA, Kakagasanov MG. The Effect of the Nanosized Oxide Filler on the Structure and Conductivity of Composite (1 – x)(LiClO4–NaClO4)–xAl2O3. Russ J Electrochem. 2023;59(8):598–603. doi:10.1134/S1023193523080050
Guseva AF, Pestereva NN, Kuznetsov DK, Boyarshinova AA, Gardt VA. Conductivity of Composites MeWO4–Al2O3 (Me = Ca, Sr). Russ J Electrochem. 2023;59(4):284–290. doi:10.1134/S1023193523040079
Zhu H, MacFarlane DR, Pringle JM, Forsyth M. Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals as Solid-State Electrolytes. Trends Chem. 2019;1(1):126–140. doi:10.1016/j.trechm.2019.01.002
Pringle JM, Howlett PC, MacFarlane DR, Forsyth M. Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals: Recent Advances. J Mater Chem. 2010;20(11):2056. doi:10.1039/b920406g
Pringle JM. Recent Progress in the Development and Use of Organic Ionic Plastic Crystal Electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15(5):1339–1351. doi:10.1039/C2CP43267F
MacFarlane DR, Forsyth M, Howlett PC, Kar M, Passerini S, Pringle JM, Ohno H, Watanabe M, Yan F, Zheng W, Zhang S, Zhang J. Ionic Liquids and Their Solid-State Analogues as Materials for Energy Generation and Storage. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1(2):15005. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2015.5
Thomas ML, Hatakeyama-Sato K, Nanbu S, Yoshizawa-Fujita M. Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals: Flexible Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Secondary Batteries. Energy Adv. 2023;2(6):748–764. doi:10.1039/D3YA00078H
Taniki R, Matsumoto K, Nohira T, Hagiwara R. All Solid-State Electrochemical Capacitors Using N,N-Dimethylpyrrolidinium Fluorohydrogenate as Ionic Plastic Crystal Electrolyte. J Power Sources. 2014;245:758–763. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.07.020
Adebahr J, Ciccosillo N, Shekibi Y, Macfarlane D, Hill A, Forsyth M. The “Filler-Effect” in Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals: Enhanced Conductivity by the Addition of Nano-Sized TiO2. Solid State Ionics. 2006;177(9–10):827–831. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2006.02.022
Pringle JM, Shekibi Y, MacFarlane DR, Forsyth M. The Influence of Different Nanoparticles on a Range of Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55(28):8847–8854. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.08.027
Stebnitskii I, Mateyshina Y, Uvarov N. The Effect of Silicon Dioxide on the Structural, Thermal and Transport Properties of an Organic Ionic Plastic Crystal (n-C4H9)4NBF4. Chim Techno Acta. 2024;11(3):202411307.
Mateyshina Y, Stebnitskii I, Uvarov N. Composite Solid Electrolytes (n-C4H9)4NBF4–Nanodiamonds. Solid State Ionics. 2024;404:116419. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2023.116419
Toby BH, Von Dreele RB. GSAS-II : The Genesis of a Modern Open-Source All Purpose Crystallography Software Package. J Appl Crystallogr. 2013;46(2):544–549. doi:10.1107/S0021889813003531
Zabinska G, Ferloni P, Sanesi M. On the Thermal Behaviour of Some Tetraalkylammonium Tetrafluoroborates. Thermochim Acta. 1987;122(1):87–94. doi:10.1016/0040-6031(87)80108-9
Matsumoto K, Harinaga U, Tanaka R, Koyama A, Hagiwara R, Tsunashima K. The Structural Classification of the Highly Disordered Crystal Phases of [Nn][BF4], [Nn][PF6], [Pn][BF4], and [Pn][PF6] Salts (Nn+ = Tetraalkylammonium and Pn+ = Tetraalkylphosphonium). Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16(43):23616–23626. doi:10.1039/C4CP03391D
Giuseppetti G, Mazzi F, Tadini C, Ferloni P, Torre S. The Crystal Structure of Tetramethylammonìum Tetrafluoroborate,(CH3)4NBF4, and the Disorder of the BF-4 Ion. Z fur Krist - Cryst Mater. 1992;202(1–4):81–88.
Himabindu B, Latha Devi NSMP, Rajini Kanth B. Microstructural Parameters from X-Ray Peak Profile Analysis by Williamson-Hall Models; A Review. Mater Today Proc. 2021;47:4891–4896. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.256
Stebnitsky IA, Uvarov NF, Mateyshina YuG. Synthesis and Study of the Physicochemical Properties of Composite Solid Electrolytes (C4H9)3CH3NBF4–Cnanodiamonds. Russ J Electrochem. 2024;60(1):18–24. doi:10.1134/S1023193524010105
Alekseev DV, Mateyshina YuG, Uvarov NF. Effect of Nanodiamond Additives on the Ionic Conductivity of the (C2H5)3CH3NBF4 Organic Salt. Russ J Electrochem. 2022;58(7):594–599. doi:10.1134/S1023193522070035
Uvarov NF, Iskakova AA, Bulina NV, Gerasimov KB, Slobodyuk AB, Kavun VYa. Ion Conductivity of the Plastic Phase of the Organic Salt [(C4H9)4N]BF4. Russ J Electrochem. 2015;51(5):491–494. doi:10.1134/S102319351505016X
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2025.12.2.09
Copyright (c) 2025 Ivan Stebnitskii, Yulia Mateyshina, Nikolai Uvarov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2025
eISSN 2411-1414
Copyright Notice







