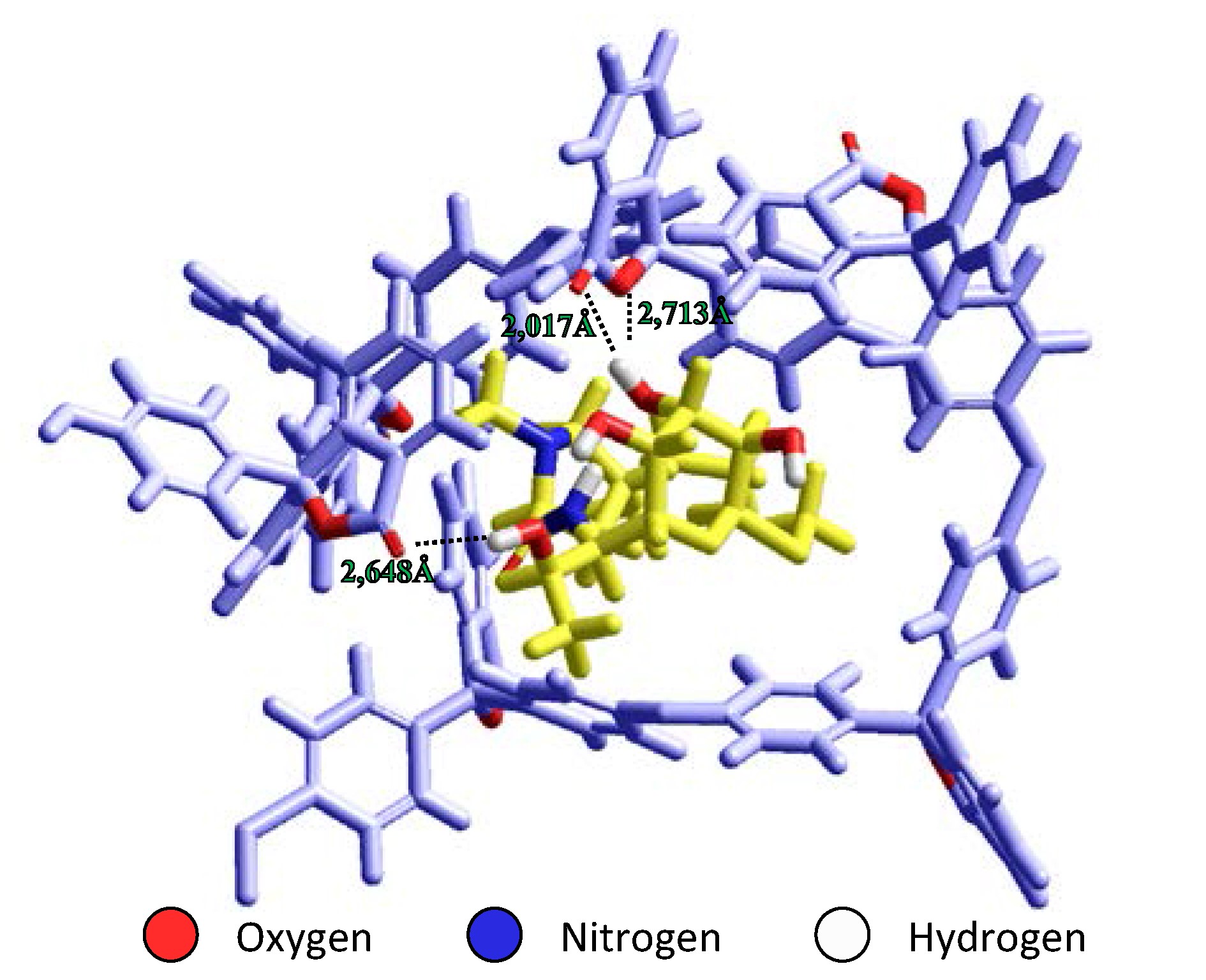
Voltammetric sensor based on molecular imprinted polymer for lincomycin determination
Abstract
Keywords
References
Pham THY, Mai TT, Nguyen HA, Chu TTH, Vu TTH, Le QH. Voltammetric determination of amoxicillin using a reduced graphite oxide nanosheet electrode. J Anal Methods Chem. 2021;2021:8823452. doi:10.1155/2021/8823452
Valenga MGP, Felsner ML, de Matos CF, de Castro EG, Galli A. Development and validation of voltammetric method for determination of amoxicillin in river water. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1138:79–88. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2020.09.020
Li H, Xu B, Wang D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Xia W, Xu S, Li Y. Immunosensor for trace penicillin G detection in milk based on supported bilayer lipid membrane modified with gold nanoparticles. J Biotechnol. 2015;203:97–103. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.03.013
Bougrini M, Florea A, Cristea C, Sandulescu R, Vocanson F, Errachid A, Bouchikhi B, Bari NE. Development of a novel sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework for tetracycline detection in honey. Food Control. 2016;59:424–429. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.06.002
Wu Y, Ye S, Hu S. Electrochemical study of lincomycin on a multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode and its determination in tablets. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006;41:820–824. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2006.01.037
Abbar JC, Meti MD, Nandibewoor ST. Anodic Voltammetric behavior of lincomycin and its electroanalytical determination in pharmaceutical dosage form and urine at gold electrode. Z Phys Chem. 2017;231(5):957–970. doi:10.1515/zpch-2015-0745
Prado TM, Foguel MV, Gonçalves LM, Sotomayor MPT. β-Lactamase-based biosensor for the electrochemical determination of benzylpenicillin in milk. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2015;210:254–258. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.12.108
Samanidou V, Nisyriou S Multi-residue methods for confirmatory determination of antibiotics in milk. J Sep Sci. 2008;31(11):2068–2090. doi:10.1002/jssc.200700647
Mohsenzadeh MS, Mohammadinejad A, Mohajeri SA. Simple and selective analysis of different antibiotics in milk using molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Food AdditContam Part A. 2018;35(10):1959–1974. doi:10.1080/19440049.2018.1508889
Bitas D, Samanidou V. Molecularly imprinted polymers as extracting media for the chromatographic determination of antibiotics in milk. Molec. 2018;23(2):316. doi:10.3390/molecules23020316
Kennedy DG, McCracken RJ, Cannavan A, Hewitt SA. Use of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in the analysis of residues of antibiotics in meat and milk. J Chromatogr A. 1998;812(1–2):77–98. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00048-X
Cañada-Cañada F, Muñoz de la Peña A, Espinosa-Mansilla A. Analysis of antibiotics in fish samples. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;395(4):987–1008. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-2872-z
Yarkaeva Y, Maistrenko V, Dymova D, Zagitova L, Nazyrov M. Polyaniline and poly(2-methoxyaniline) based molecular imprinted polymer sensors for amoxicillin voltammetric determination. Electrochim Acta. 2022;433:141222. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141222
Zagitova L, Maistrenko V, Yarkaeva Y, Zagitov V, Zilberg R, Kovyazin P, Parfenova L. Novel chiral voltammetric sensor for tryptophan enantiomers based on 3-neomenthylindene as recognition element. J Electroanal Chem. 2021;880:114939. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114939
Yarkaeva Y, Maistrenko V, Zagitova L, Nazyrov M, Berestova T. Voltammetric sensor system based on Cu(II) and Zn(II) amino acid complexes for recognition and determination of atenolol enantiomers. J Electroanal Chem. 2021;903:115839. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115839
Yarkaeva Y, Islamuratova E, Zagitova L, Gus’kov V, Zil’berg R, Maistrenko V. A Sensor for the recognition and determination of tryptophan enantiomers based on carbon-paste electrode modified by enantiomorphic crystals of bromotriphenylmethane. J Anal Chem. 2021;76(11):1345–1354. doi:10.1134/S1061934821110162
Zagitova L, Yarkaeva Y, Zagitov V, Nazyrov M, Gainanova S, Maistrenko V. Voltammetric chiral recognition of naproxen enantiomers by N-tosylproline functionalized chitosan and reduced graphene oxide based sensor. J Electroanal Chem. 2022;992:116774. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116744
Benachio I, Lobato A, Goncalves LM. Employing molecularly imprinted polymers in the development of electroanalytical methodologies for antibiotic determination. J Mol Recognit. 2021;34:2878. doi:10.1002/jmr.2878
Wulff G. Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: origin, features and perspectives. Microchim Acta. 2013;180(15–16):1359–1370. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0992-9
Baeza-Fonte AN, Garcés-Lobo I, Luaces-Alberto MD, Gonçalves LM, Sotomayor M, Valdés-González AC. Determination of cephalosporins by UHPLC-DAD using molecularly imprinted polymers. J Chromatogr Sci. 2018;56(2):187–197. doi:10.1093/chromsci/bmx099
Alenazi NA, Manthorpe JM, Lai EPC. Selectivity enhancement in molecularly imprinted polymers for binding of bisphenol A. Sensors. 2016;16(10):1697. doi:10.3390/s16101697
Gavrila AM, Stoica EB, Iordache TV, Sârbu A. Modern and dedicated methods for producing molecularly imprinted polymer layers in sensing applications. Appl Sci. 2022;12:3080. doi:10.3390/app12063080
BelBruno J. Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev. 2019;119:94–119. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Kraikin V, Fatykhov A, Gileva N, Kravchenko A, Salazkin S. NMR study of dyadic and triadic splitting in copoly(arylene)phthalides based on diphenyl oxide and diphenyl sulfide. Magn Reson Chem. 2020;59(1):61–73. doi:10.1002/mrc.5079
Salazkin S, Shaposhnikova V, Machulenko L, Gileva N, Kraikin V, Lachinov A. Synthesis of polyarylenephthalides prospective as smart polymers. Polym Sci Ser A. 2008;50(3):243–259. doi:10.1134/S0965545X08030024
Gileva N, Kraikin V, Sedova E, Lobov M, Kuznetsov S, Salazkin S. Control over the composition and microstructure of copoly(arylene phthalides). Russ J Appl Chem. 2005;78(10):1683–1686. doi:10.1007/s11167-005-0586-3
Salikhov R, Zilberg R, Mullagaliev I, Salikhov T, Teres Y. Nanocomposite thin film structures based on polyarylenephthalide with SWCNT and graphene oxide fillers. Mendeleev Commun. 2022;32:520–522. doi:10.1016/j.mencom.2022.07.029
Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG. Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 10th Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. 256 p.
Luo H, Li H, Ge Q, Cong H, Tao Z, Liu M. An electrochemical sensor for enantio-recognition of tyrosine based on a chiral macrocycle functionalized rGO. Microchem J. 2021;164:105949. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2021.105949
Wu YY, Zhao FQ, Ju XH, A comparison of the accuracy of semi-empirical PM3, PDDG and PM6 methods in predicting heats of formation for organic compounds. J Mex Chem Soc. 2014;58:223–229. doi:10.29356/jmcs.v58i2.182
Girondi NG, Barreto F, Pigatto MC, Dalla Costa T. Sensitive analytical method to quantify clindamycin in plasma and microdialysate samples: Application in a preclinical pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018;153:57–62. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.02.005
Hu Y, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Liao C, Jiang G. A short review of human exposure to antibiotics based on urinary biomonitoring. Sci Total Environ. 2022;830:154775. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154775
Gouri SS, Venkatachalam D, Dumka VK. Pharmacokinetics of lincomycin following single intravenous administration in buffalo calves. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2014;46:1099–1102. doi:10.1007/s11250-014-0595-4
Boonsong K, Chuanuwatanakul S, Wangfuengkanagul N, Chailapakul O. Electroanalysis of lincomycin using boron-doped diamond thin film electrode applied to flow injection system. Sensors Actuators B. 2005;108:627–632. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2004.12.087
Li N, Song J, Wei Guo, Xu M. Study and application of parallel catalytic hydrogen wave of lincomycin in the presence of persulfate. Microchem J. 2004;77:23–28. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2003.10.001
Wang X, Yang T, Jiao K. Electrochemical study of lincomycin on Au-PtNPs/nanoPAN/ Chitosan nanocomposite membrane and its determination in injections. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2010;26(3):371–375.
Li S, Liu C, Yin G, Zhang Q, Luo J, Wu N. Aptamer-molecularly imprinted sensor base on electrogenerated chemiluminescence energy transfer for detection of lincomycin. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2017;91:687–691. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.038
Liu X-P, Huang B, Mao C-J, Chen J-S, Jin B-K. Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for lincomycin antigen detection by using a SnO2/chitosan/g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Talanta. 2021;233:122546. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122546
Wei M, Du X, Zhang Y, Shan X, Wang W, Chen Y, Jiang D, Xu F, Shiigi H, Chen Z. Ultrasensitive self-driven photoelectrochemical aptasensor for lincomycin detection based on oxygen vacancy-tunable BiOBr nanosheet coupled with dual-function of N-doped Ti3C2 quantum dots. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2022;12:100266. doi:10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100266
Wen Z, Ding L, Zhang M, You F, Yuan R, Wei J, Qian J, Wang K. A membrane/mediator-free high-power density dual-photoelectrode PFC aptasensor for lincomycin detection in milk and chicken. Anal Chim Acta. 2023;1245:340880. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2023.340880
Leng Y, Hu F, Ma C, Du C, Ma L, Xu J, Lin Q, Sang Z, Lu Z. Simple, rapid, sensitive, selective and label-free lincomycin detection by using HAuCl4 and NaOH. RSC Adv. 2019;9:28248–28252. doi:10.1039/C9RA04095A
Li J, Luo M, Jin C, Zhang P, Yang H, Cai R, Tan W. Plasmon-Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence of PTP-Decorated Eu MOF-Based Pt-tipped au bimetallic nanorods for the lincomycin Assay. Eur Food Res Technol. 2022;248:2157–2165. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c21528
Shi Q, Tao C, Kong D. Multiplex SERS‑based lateral flow assay for one‑step simultaneous detection of neomycin and lincomycin in milk. Eur Food Res Technol. 2022;248:2157–2165. doi:10.1007/s00217-022-04038-3
Fan Y, Liu Z, Wang J, Cui C, Hu L. An “off–on” electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for determination of lincomycin based on CdS QDs/carboxylated g-C3N4. Microchim Acta. 2023;190(1):11. doi:10.1007/s00604-022-05587-w
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2023.10.2.10
Copyright (c) 2023 Yulia A. Yarkaeva, Daria A. Dymova, Marat I. Nazyrov, Liana R. Zagitova, Valery N. Maistrenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2025
eISSN 2411-1414
Copyright Notice







